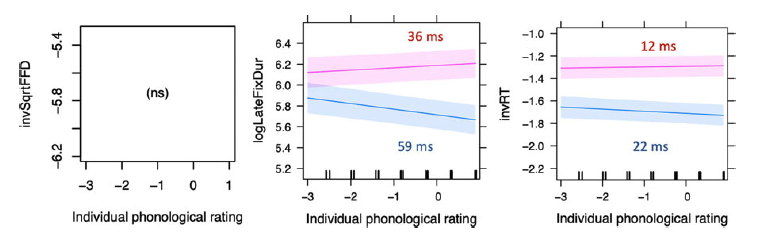
This study compared patterns of non-selective cross-language activation in L1 and L2 word recognition with different-script bilinguals. The aim was to determine (1) whether lexical processing is non-selective in the L1 (as in L2), and (2) if the same cross-linguistic factors affected processing similarly in each language. To examine the time course of activation, eye movements were tracked during lexical decision. Thirty-two Japanese-English bilinguals responded to 250 words and 250 nonwords in Japanese and English. The same participants and items (i.e., cognate translation equivalents) were used to directly compare L1 and L2 processing. Response latencies as well as eye movements representing early and late processing were analyzed using mixed-effects regression modeling (Baayen et al., 2008). Similar cross-linguistic effects, namely cognate word frequency, phonological similarity, and semantic similarity, were found in both languages. These factors affected processing to different degrees in each language, however. While cognate frequency was significant as early as the first fixation, effects of cross-linguistic phonological and semantic similarity arose later in time. Increased phonological similarity slowed responses in L2 but speeded them in L1, while greater semantic overlap was facilitatory in both languages. Results are discussed from the perspective of the BIA+ model of visual word recognition.
Taylor, J. & Mukai, Y. (2023). Bidirectional cross-linguistic influence in Japanese-English bilingual word recognition: An eye movement study. Applied Psycholinguistics, 44(5), 635-667. doi:10.1017/S0142716423000188. Post-print available on VIUSpace.
