We are particularly interested in the following aspects of language and experimental methods to understand how sounds or words are represented/processed in the mind. Specifically, how different types of variables are integrated into the representation/processing of sounds or words and how these factors inhibit or facilitate speech communication.
- Spontaneous Speech (e.g., phonetic reduction)
- Orthography (e.g., phonology-to-orthography consistency)
- L2 Pronunciation and Comprehension (e.g., the variability in the temporal organization of vowels and consonants & production and perception of L2 speech fluency and accent),
- Task-Evoked Pupillary Response (i.e., pupillometry)
- Japanese Phonetics and Psycholinguistics (e.g., production and perception of voiced stops and nasals)
The role of phonology-to-orthography consistency in predicting the degree of pupil dilation induced in processing reduced and unreduced speech
In the present study, we investigate the effect of pronunciation-to-spelling consistency for reduced and unreduced pronunciations in L1 and L2 listeners of a logographic language. More precisely, we compare L1 and L2 Japanese listeners to probe whether they use orthographic information differently when processing reduced and unreduced speech.
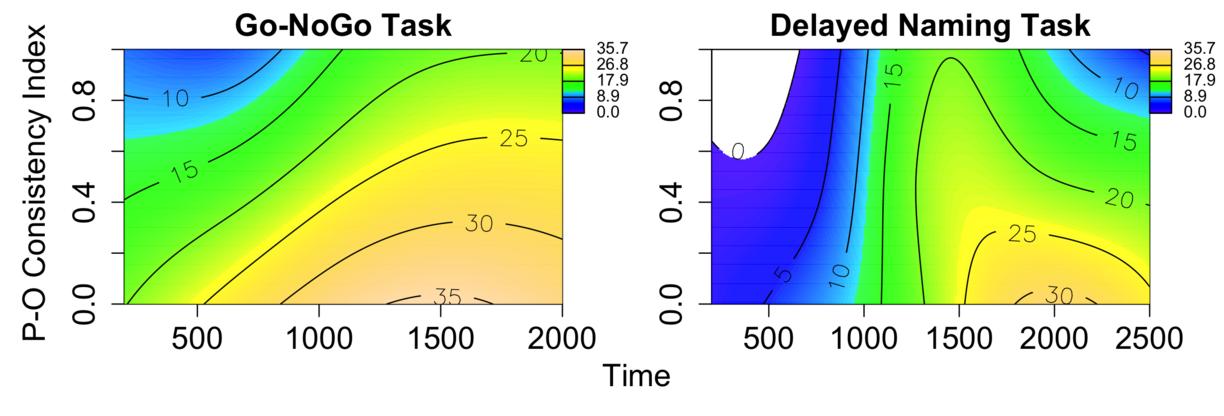
Mukai, Y., Järvikivi, J., & Tucker, B.V. (2023). The role of phonology-to-orthography consistency in predicting the degree of pupil dilation induced in processing reduced and unreduced speech. Applied Psycholinguistics, 44(5), 784-815. doi:10.1017/S0142716423000279
Bidirectional cross-linguistic influence with different-script languages: Evidence from eye tracking
This study compared patterns of non-selective cross-language activation in L1 and L2 word recognition with different-script bilinguals. The aim was to determine (1) whether lexical processing is non-selective in the L1 (as in L2), and (2) if the same cross-linguistic factors affected processing similarly in each language.
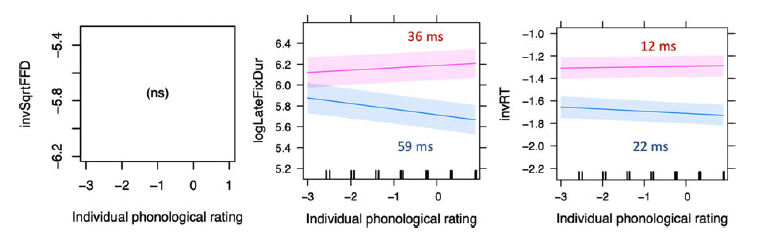
Taylor, J. & Mukai, Y. (2023). Bidirectional cross-linguistic influence in Japanese-English bilingual word recognition: An eye movement study. Applied Psycholinguistics, 44(5), 635-667. doi:10.1017/S0142716423000188. Post-print available on VIUSpace.
Spontaneous Speech
Phonetic research investigates how speakers and listeners use speech to convey messages. The speech produced to encode a particular message can vary wildly. Understanding and explaining the phonetic variability embodied in this example is one of the main motivations for this Element.


Tucker, B.V. & Mukai, Y. (2023). Spontaneous Speech (Elements in Phonetics). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi.org/10.1017/9781108943024.
Examining cognitive control in people with aphasia: Evidence from pupillometry
Wilson.C., Mukai, Y., Figeys, M., Suleman, S., Garcia, R., & Kim, E.S. (in preparation). Examining cognitive control in people with aphasia: Evidence from pupillometry
Durational variability of spontaneous and read speech: Comparison between English and Japanese
Mukai, Y., Brenner, D., & Tucker, B.V. (in preparation). Durational variability of spontaneous and read speech: Comparison between English and Japanese
Phonetic variability of stops and nasals in Japanese across a range of speaking styles.
Mukai, Y., & Tucker, B.V. (in preparation). Phonetic variability of stops and nasals in Japanese across a range of speaking styles.
